Disparity Map
As I had mentioned in earlier posts that I was working on Stereo Images, disparity and depth images, I will elaborate about disparity maps and show how to compute it using OpenCV.
What is Disparity Map?
Disparity refers to the difference in location of an object in corresponding two (left and right) images as seen by the left and right eye which is created due to parallax (eyes’ horizontal separation). The brain uses this disparity to calculate depth information from the two dimensional images.
In short, The disparity of a pixel is equal to the shift value that leads to minimum sum-of-squared-differences for that pixel.
The term disparity was originally used to describe the 2D vector between the positions of corresponding features seen by the left and right eyes. It is inversely proportional to depth, and it is possible to define a mapping from an (x,y,d) triple to a three-dimensional position.
Calculating Disparity Map
The images are padded with a “frame” of zero pixels to facilitate the window operation (SSD/SAD) at the border.
SSD - Sum of Squared Differences SAD - Sum of Absolute Differences
First, squared difference or absolute difference is calcluated for each pixel and then all the values are summed over a window W.
For each shift value of the right image, there is an SSD/SAD map equal to the size of the image. The disparity map is a 2D map reduced from 3D space. The disparity of a pixel is equal to the shift value that leads to minimum SSD/SAD for that pixel. The figure below shows an example of different SSD values of a single pixel at different shifted values.
Calculating Disparity Map using OpenCV
In OpenCV, to calculate disparity map, it has StereoBM and StereoSGBM.
Stereo BM stands for block matching algorithm. Stereo SGBM stands for semi block matching algorithm.
Include required headers.
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/contrib/contrib.hpp"
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Load Images and initialize parameters.
Mat img1, img2, g1, g2;
Mat disp, disp8;
img1 = imread("leftImage.jpg");
img2 = imread("rightImage.jpg");
cvtColor(img1, g1, CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img2, g2, CV_BGR2GRAY);
Articles related to disparity maps and 3D imaging
Calculate depth using Stereo Ranging
Learn what stereo ranging is and how to use it to find the distance of the object from the cameras!
Detect fingertips in depth maps
Write algorithm to detect contours and hull points in order to detect fingertips in a depth map generated by Kinect.
StereoBM
You can set parameters for StereoBM.
StereoBM sbm;
sbm.state->SADWindowSize = 9;
sbm.state->numberOfDisparities = 112;
sbm.state->preFilterSize = 5;
sbm.state->preFilterCap = 61;
sbm.state->minDisparity = -39;
sbm.state->textureThreshold = 507;
sbm.state->uniquenessRatio = 0;
sbm.state->speckleWindowSize = 0;
sbm.state->speckleRange = 8;
sbm.state->disp12MaxDiff = 1;
- minDisparity – Minimum possible disparity value.
- numDisparities – Maximum disparity minus minimum disparity. This parameter must be divisible by 16.
- SADWindowSize – Matched block size. It must be an odd number >=1 .
- disp12MaxDiff – Maximum allowed difference (in integer pixel units) in the left-right disparity check.
- preFilterCap – Truncation value for the prefiltered image pixels.
- uniquenessRatio – Margin in percentage by which the best (minimum) computed cost function value should “win” the second best value to consider the found match correct. Normally, a value within the 5-15 range is good enough.
- speckleWindowSize – Maximum size of smooth disparity regions to consider their noise speckles and invalidate.
- speckleRange – Maximum disparity variation within each connected component.
And compute Disparity. Since Disparity will be either CV_16S or CV_32F, it needs to be compressed and normalized to CV_8U
sbm(g1, g2, disp);
normalize(disp, disp8, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX, CV_8U);
Stereo SGBM
In a similar manner, StereoSGBM can be used to compute Disparity. Siddharth has been working on SGBM parameters and he came up with a set of parameters which can be used in all the scenarios to get a good disparity map. So I’m updating those values here.
StereoSGBM sgbm;
sgbm.SADWindowSize = 5;
sgbm.numberOfDisparities = 192;
sgbm.preFilterCap = 4;
sgbm.minDisparity = -64;
sgbm.uniquenessRatio = 1;
sgbm.speckleWindowSize = 150;
sgbm.speckleRange = 2;
sgbm.disp12MaxDiff = 10;
sgbm.fullDP = false;
sgbm.P1 = 600;
sgbm.P2 = 2400;
Notice there are few parameters different from StereoBM. Compute Disparity and normalize. You should look at OpenCV documentation for detailed information.
sgbm(g1, g2, disp);
normalize(disp, disp8, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX, CV_8U);
And, finishing touch, show the images.
imshow("left", img1);
imshow("right", img2);
imshow("disp", disp8);
Here’s the image where I have used StereoSGBM.
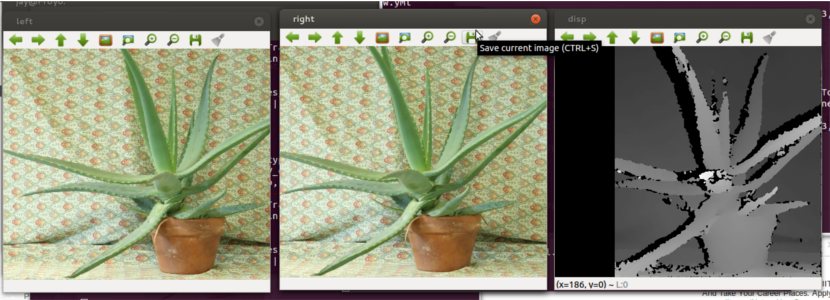
You can find Python code here and C++ code here. Other useful links. http://davidpritchard.org/graphics/msc_thesis/4_Disparity_Map.html https://sites.google.com/site/5kk73gpu2010/assignments/stereo-vision#TOC-Update-Disparity-Map
P.S. Also working on Depth images. Wait for upcoming posts.
Playing around with Android UI
Articles focusing on Android UI - playing around with ViewPagers, CoordinatorLayout, meaningful motions and animations, implementing difficult customized views, etc.


