Stereo Calibration
Whenever working with stereoscopy, it is a necessity to calibrate the cameras and get the required intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
This is a so-called pinhole camera model. A scene view is formed by projecting 3D points into the image plane using a perspective transformation.
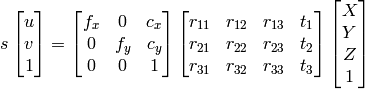
What is Camera Calibration?
In the manufacturing process of a camera, there might be some distortions invloved due to inaccurate positioning of the lens or inaccuracy in manufacturing parabolic lens. Read more about distortion on AI shack
Calibrating the camera gives us some specific values which can be used to measure distances in length units and not in pixels. Goal of calibration to find out intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the camera.
Intrinsic Parameters
Intrinsic parameters include focal length, image format and principal point. This is the intrinsic matrix.
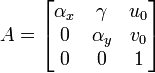
αx and αy denote focal length in x direction and y direction respectively. u0 and v0 denote the principal point which would be ideally in the center.
Extrinsic Parameters
R and T are the extrinsic parameters which represent the coordinate transormation from 3D world to 3D camera model.

Camera Calibration
One standard procedure to calibrate camera is to use a chessboard pattern. It is easier to calibrate using chessboard pattern because it is flat so no concerns of depth, it is easier to extract corner points as they are extensively defined. All the corners lie on the same line. Many different poses are used to get a better calibration.
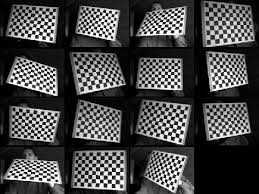
Calibration using OpenCV
OpenCV has a great support for calibration and there’s is a very convinient way to do it.
Include necessary libraries
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;Main function
int numBoards; // number of different poses
int board_w; // number of horizontal corners
int board_h; // number of vertical corners
Size board_sz = Size(board_w, board_h);
int board_n = board_w*board_h;
vector<vector<Point3f> > objectPoints;
vector<vector<Point2f> > imagePoints;
vector<Point2f> corners;imagePoints represent location of the detected corners in the image.
objectPoints represent the real location of the corners in 3D.
Initialize Camera and define image containers.
Mat img, gray;
VideoCapture cap = VideoCapture(1);
int success = 0;
int k = 0;
bool found = false;objectPoints should contain physical location of each corners but since we don’t know that so we assign constant positions to all the corners and assume that camera is moving.
vector<Point3f> obj;
for (int j=0; j<board_n; j++)
{
obj.push_back(Point3f(j/board_w, j%board_w, 0.0f));
}Get data for calibration
cap >> img;
cvtColor(img, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
found = findChessboardCorners(gray, board_sz, corners,
CV_CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | CV_CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS);
// returns bool if found or not
if (found)
{
imagePoints.push_back(corners);
objectPoints.push_back(obj);
printf ("Corners stored\n");
success++;
}Draw Corners on chessboard and show
cornerSubPix(gray, corners, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1),
TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS | CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 30, 0.1));
drawChessboardCorners(gray, board_sz, corners, found);
imshow("corners", gray); Chessboard Corners in Calibration
Chessboard Corners in Calibration
You found corners for one pose. You need to add a loop over this and get numBoards poses.
Start Calibration
Mat CM = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1);
Mat D;
vector<Mat> rvecs, tvecs;
CM.at<float>(0, 0) = 1;
CM.at<float>(1, 1) = 1;
calibrateCamera(objectPoints, imagePoints, img.size(), CM, D, rvecs, tvecs);CMis 3x3 floating-point camera matrix.Dis the vector of distortion coefficients.rvecsis vector of rotation vectors estimated for each pattern view.tvecsis vector of translation vectors estimated for each pattern view.
Undistort the image.
Mat imgU;
undistort(img, imgU, CM, D);Save Calibration Data.
FileStorage fs1("mycalib.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
fs1 << "CM" << CM;
fs1 << "D" << D;
fs1.release();Stereo Calibration
Stereo calibration is similar to single camera calibration but it invloves more steps and gives complete intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
Follow the procedure for single camera calibration till cameraCalibration method. You need to define two imagePoints vectors and need to find chessboard in both images.
found1 = findChessboardCorners(img1, board_sz, corners1,
CV_CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | CV_CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS);
found2 = findChessboardCorners(img2, board_sz, corners2,
CV_CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | CV_CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS);
if (found1 && found2)
{
imagePoints1.push_back(corners1);
imagePoints2.push_back(corners2);
objectPoints.push_back(obj);
printf ("Corners stored\n");
success++;
}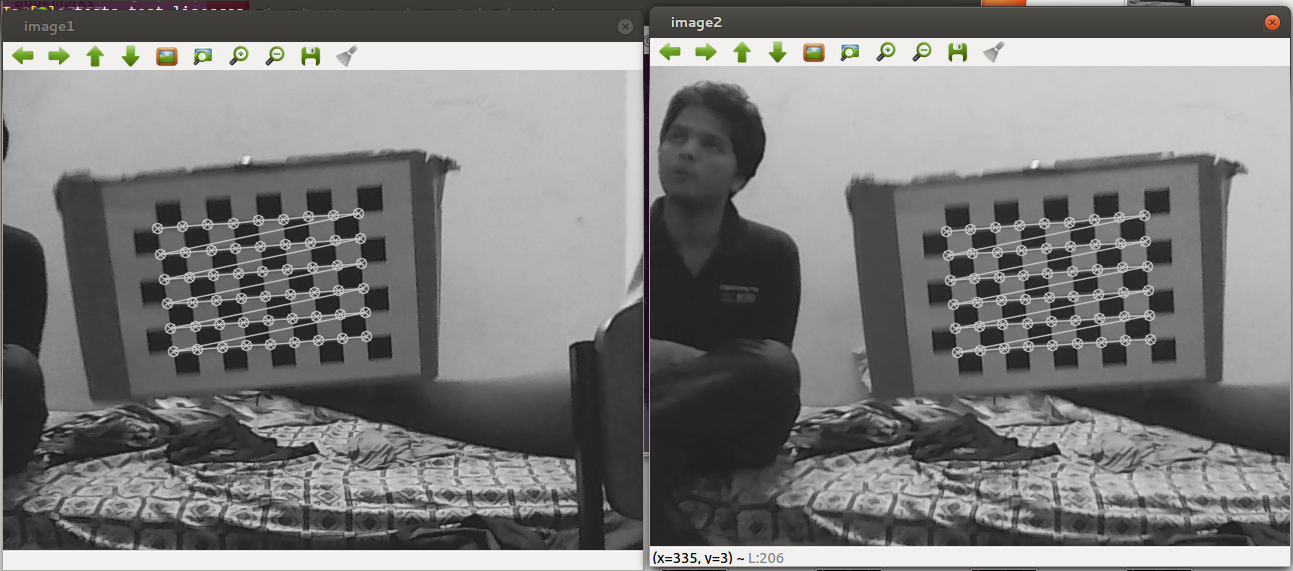 Chessboard Corners in Stereo Images.
Chessboard Corners in Stereo Images.
Start Stereo Calibration.
Mat CM1 = Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1);
Mat CM2 = Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1);
Mat D1, D2;
Mat R, T, E, F;
stereoCalibrate(objectPoints, imagePoints1, imagePoints2,
CM1, D1, CM2, D2, img1.size(), R, T, E, F,
cvTermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER+CV_TERMCRIT_EPS, 100, 1e-5),
CV_CALIB_SAME_FOCAL_LENGTH | CV_CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST);CM1- Camera Matrix of first camera.CM2- Camera Matrix of second camera.D1- Distortion coeff matrix of first camera.D2- Distortion coeff matrix of second camera.R- Rotation Matrix between first and second camera coordinate systems.T- Translation vector between the coordinate systems of the cameras.E- Essential matrix.F- Fundamental matrix.
Start Stereo Rectification.
stereoRectify computes rectification transforms for each calibrated stereo camera.
Mat R1, R2, P1, P2, Q;
stereoRectify(CM1, D1, CM2, D2, img1.size(), R, T, R1, R2, P1, P2, Q);R1- 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the first camera.R2- 3x3 rectification transform (rotation matrix) for the second camera.P1- 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the first camera.P2- 3x4 projection matrix in the new (rectified) coordinate systems for the second camera.Q– 4x4 disparity-to-depth mapping matrix.
Store Calibration Data.
FileStorage fs1("mystereocalib.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
fs1 << "CM1" << CM1;
fs1 << "CM2" << CM2;
fs1 << "D1" << D1;
fs1 << "D2" << D2;
fs1 << "R" << R;
fs1 << "T" << T;
fs1 << "E" << E;
fs1 << "F" << F;
fs1 << "R1" << R1;
fs1 << "R2" << R2;
fs1 << "P1" << P1;
fs1 << "P2" << P2;
fs1 << "Q" << Q;
fs1.release();Undistort and remap image.
Mat map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y;
Mat imgU1, imgU2;
initUndistortRectifyMap(CM1, D1, R1, P1, img1.size(), CV_32FC1, map1x, map1y);
initUndistortRectifyMap(CM2, D2, R2, P2, img1.size(), CV_32FC1, map2x, map2y);
remap(img1, imgU1, map1x, map1y, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar());
remap(img2, imgU2, map2x, map2y, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar());Once you have calibrated your camera, you can use the saved parameters in other applications where you need 3D data using Stereo Vision. eg. getting depth of any object.
You can find C++ source code on my GitHub.
Other important links
Image courtsey - OpenCV docs, stackoverflow.
P.S. Need to work on Machine Learning.
Playing around with Android UI
Articles focusing on Android UI - playing around with ViewPagers, CoordinatorLayout, meaningful motions and animations, implementing difficult customized views, etc.


